Came across an interesting error the other night while on call, as I had a host in a cluster that VM’s could not vMotion off of either manually or through DRS. I was seeing the following error message in vSphere:
The source detected that the destination failed to resume.
vMotion migration [-1062731518:1481069780557682] failed: remote host <192.168.1.2> failed with status Failure.
vMotion migration [-1062731518:1481069780557682] failed to asynchronously receive and apply state from the remote host: Failure.
Failed waiting for data. Error 195887105. Failure.
- While tailing the host.d log on the source host I was seeing the following error:
2016-12-09T19:44:40.373Z warning hostd[2B3E0B70] [Originator@6876 sub=Libs] ResourceGroup: failed to instantiate group with id: -591724635. Sysinfo error on operation return ed status : Not found. Please see the VMkernel log for detailed error information
- While tailing the host.d log on the destination host, I was seeing the following error:
2016-12-09T19:44:34.330Z info hostd[33481B70] [Originator@6876 sub=Snmpsvc] ReportVMs: processing vm 223
2016-12-09T19:44:34.330Z info hostd[33481B70] [Originator@6876 sub=Snmpsvc] ReportVMs: serialized 36 out of 36 vms
2016-12-09T19:44:34.330Z info hostd[33481B70] [Originator@6876 sub=Snmpsvc] GenerateFullReport: report file /tmp/.vm-report.xml generated, size 915 bytes.
2016-12-09T19:44:34.330Z info hostd[33481B70] [Originator@6876 sub=Snmpsvc] PublishReport: file /tmp/.vm-report.xml published as /tmp/vm-report.xml
2016-12-09T19:44:34.330Z info hostd[33481B70] [Originator@6876 sub=Snmpsvc] NotifyAgent: write(33, /var/run/snmp.ctl, V) 1 bytes to snmpd
2016-12-09T19:44:34.330Z info hostd[33481B70] [Originator@6876 sub=Snmpsvc] GenerateFullReport: notified snmpd to update vm cache
2016-12-09T19:44:34.330Z info hostd[33481B70] [Originator@6876 sub=Snmpsvc] DoReport: VM Poll State cache - report completed ok
2016-12-09T19:44:40.317Z warning hostd[33081B70] [Originator@6876 sub=Libs] ResourceGroup: failed to instantiate group with id: 727017570. Sysinfo error on operation returne d status : Not found. Please see the VMkernel log for detailed error information
- While tailing the destination vmkernel.log host, I was seeing the following error:
2016-12-09T19:44:22.000Z cpu21:35086 opID=b5686da8)World: 15516: VC opID AA8C46D5-0001C9C0-81-91-cb-a544 maps to vmkernel opID b5686da8
2016-12-09T19:44:22.000Z cpu21:35086 opID=b5686da8)Config: 681: "SIOControlFlag2" = 1, Old Value: 0, (Status: 0x0)
2016-12-09T19:44:22.261Z cpu21:579860616)World: vm 579827968: 1647: Starting world vmm0:oats-agent-2_(e00c5327-1d72-4aac-bc5e-81a10120a68b) of type 8
2016-12-09T19:44:22.261Z cpu21:579860616)Sched: vm 579827968: 6500: Adding world 'vmm0:oats-agent-2_(e00c5327-1d72-4aac-bc5e-81a10120a68b)', group 'host/user/pool34', cpu: shares=-3 min=0 minLimit=-1 max=4000, mem: shares=-3 min=0 minLimit=-1 max=1048576
2016-12-09T19:44:22.261Z cpu21:579860616)Sched: vm 579827968: 6515: renamed group 5022126293 to vm.579860616
2016-12-09T19:44:22.261Z cpu21:579860616)Sched: vm 579827968: 6532: group 5022126293 is located under group 5022124087
2016-12-09T19:44:22.264Z cpu21:579860616)MemSched: vm 579860616: 8112: extended swap to 46883 pgs
2016-12-09T19:44:22.290Z cpu20:579860616)Migrate: vm 579827968: 3385: Setting VMOTION info: Dest ts = 1481312661276391, src ip = <192.168.1.2> dest ip = <192.168.1.17> Dest wid = 0 using SHARED swap
2016-12-09T19:44:22.293Z cpu20:579860616)Hbr: 3394: Migration start received (worldID=579827968) (migrateType=1) (event=0) (isSource=0) (sharedConfig=1)
2016-12-09T19:44:22.332Z cpu0:33670)MigrateNet: vm 33670: 2997: Accepted connection from <::ffff:192.168.1.2>
2016-12-09T19:44:22.332Z cpu0:33670)MigrateNet: vm 33670: 3049: data socket size 0 is less than config option 562140
2016-12-09T19:44:22.332Z cpu0:33670)MigrateNet: vm 33670: 3085: dataSocket 0x430610ecaba0 receive buffer size is 562140
2016-12-09T19:44:22.332Z cpu0:33670)MigrateNet: vm 33670: 2997: Accepted connection from <::ffff:192.168.1.2>
2016-12-09T19:44:22.332Z cpu0:33670)MigrateNet: vm 33670: 3049: data socket size 0 is less than config option 562140
2016-12-09T19:44:22.332Z cpu0:33670)MigrateNet: vm 33670: 3085: dataSocket 0x4306110fab70 receive buffer size is 562140
2016-12-09T19:44:22.332Z cpu0:33670)VMotionUtil: 3995: 1481312661276391 D: Stream connection 1 added.
2016-12-09T19:44:24.416Z cpu1:32854)elxnet: elxnet_allocQueueWithAttr:4255: [vmnic0] RxQ, QueueIDVal:2
2016-12-09T19:44:24.416Z cpu1:32854)elxnet: elxnet_startQueue:4383: [vmnic0] RxQ, QueueIDVal:2
2016-12-09T19:44:24.985Z cpu12:579860756)VMotionRecv: 658: 1481312661276391 D: Estimated network bandwidth 471.341 MB/s during pre-copy
2016-12-09T19:44:24.994Z cpu4:579860755)VMotionSend: 4953: 1481312661276391 D: Failed to receive state for message type 1: Failure
2016-12-09T19:44:24.994Z cpu4:579860755)WARNING: VMotionSend: 3979: 1481312661276391 D: failed to asynchronously receive and apply state from the remote host: Failure.
2016-12-09T19:44:24.994Z cpu4:579860755)WARNING: Migrate: 270: 1481312661276391 D: Failed: Failure (0xbad0001) @0x4180324c6786
2016-12-09T19:44:24.994Z cpu4:579860755)WARNING: VMotionUtil: 6267: 1481312661276391 D: timed out waiting 0 ms to transmit data.
2016-12-09T19:44:24.994Z cpu4:579860755)WARNING: VMotionSend: 688: 1481312661276391 D: (9-0x43ba40001a98) failed to receive 72/72 bytes from the remote host <192.168.1.2>: Timeout
2016-12-09T19:44:24.998Z cpu4:579860616)WARNING: Migrate: 5454: 1481312661276391 D: Migration considered a failure by the VMX. It is most likely a timeout, but check the VMX log for the true error.
We are using the vSphere distributed switch in our environment, and each host has a vmk dedicated to vMotion traffic only, so this was my first test, verified the IP and subnet for the vmk on the source/destination hosts, and I was successfully able to ping using vmkping to the destination host, and tested the connection both ways.
The second test completed was to power off a VM, and test its ability to vMotion off of the host – this worked. When I powered the VM back on it immediately went back to the source host. I then tried to vMotion the VM again while it was powered on from the affected source host, and move it to the destination host like I had before, and to my surprise it worked now. Tested this process with a few other VMs for consistency. I tried to restart a VM on the affected host, and then move it off to another host, but this did not work.
My final test was to vMotion a VM from a different host to the affected host. This worked as well, and I was even able to vMotion off from that affected host again.
In our environment we have a Trend-micro agent VM and a GI VM running on each host. I logged into the vSphere web-client to look at the status of the Trend-micro VM and there was no indication of an error, I found the same status checking the GI vm.
Knowing we have had issues with Trend-micro in the past, I powered down the Trend-micro VM running on the host, and attempted a manual vMotion of a test VM I knew couldn’t move before – IT WORKED. Tried another with the same result. Put the host into maintenance mode to try and evacuate the rest of the customer VMs off from it with success!
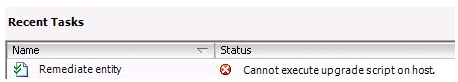
To wrap all of this up, the Trend-micro agent VM running on the esxi6 host was preventing other VMs from vMotioning off either manually or through DRS. Once the trend-micro agent VM was powered off, I was able to evacuate the host.










You must be logged in to post a comment.